Which entities are not subject to franchise tax?
Entities Not Subject to Franchise Tax. The following entities do not file or pay franchise tax: sole proprietorships (except for single member LLCs); general partnerships when direct ownership is composed entirely of natural persons (except for limited liability partnerships);
Are unincorporated partnerships subject to franchise tax?
general partnerships when direct ownership is composed entirely of natural persons (except for limited liability partnerships); real estate mortgage investment conduits and certain qualified real estate investment trusts; unincorporated political committees. Franchise tax is based on a taxable entity’s margin.
Who has to pay franchise tax in Texas?
Each taxable entity formed in Texas or doing business in Texas must file and pay franchise tax.
Which entities are not subject to the Texas tax code?
Entities not subject to the tax include sole proprietorships, general partnerships owned entirely by natural persons, passive entities defined under Texas law, grantor trusts, estates of natural persons, and escrows (TX Tax Code §171.0002 (b)). For Texas purposes, grantor trusts are defined by Secs. 671 and 7701 (a) (30) (E).

Who is exempt from Texas franchise tax?
A nonprofit corporation organized under the Development Corporation Act of 1979 (Article 5190.6, Vernon's Texas Civil Statutes) is exempt from franchise and sales taxes. The sales tax exemption does not apply to the purchase of an item that is a project or part of a project that the corporation leases, sells or lends.
What entities are subject to Texas franchise tax?
The franchise tax is imposed on the following entities that are either organized in Texas or doing business in Texas: • corporations; • limited liability companies (LLCs), including single member and series LLCs; • banks; • state limited banking associations; 1 Page 2 • savings and loan associations; • S corporations; ...
Who must pay franchise tax in Texas?
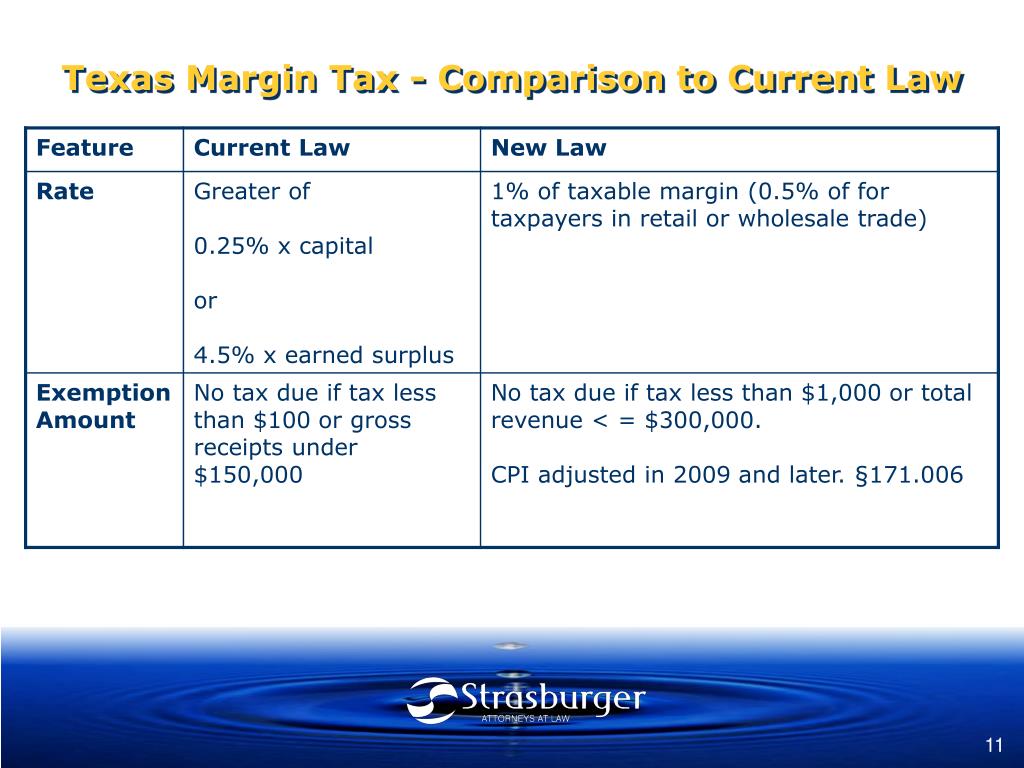
The Texas Franchise Tax is calculated on a company's margin for all entities with revenues above $1,230,000. The margin's threshold is subject to change each year. The margin can be calculated in one of the following ways: Total Revenue Multiplied by 70 Percent.
Are limited partnerships subject to Texas franchise tax?
Texas Tax Code (TTC) 171.0001(11-a). Are family limited partnerships subject to the franchise tax? A family limited partnership is a taxable entity unless it meets the criteria of a passive entity under TTC 171.0003.
How are partnerships taxed in Texas?
In Texas, most partnerships are subject to the franchise tax. Generally speaking, the only exception is a general partnership directly and solely owned by natural persons. Regardless of the type of partnership, individual partners personally owe no state tax on partnership income distributed to them.
What is a disregarded entity for Texas franchise tax?
Disregarded Entities Therefore, partnerships, LLCs and other entities that are disregarded for federal income tax purposes are considered separate legal entities for franchise tax reporting purposes. The separate entity is responsible for filing its own franchise tax report unless it is a member of a combined group.
How do I know if I need to pay franchise tax in Texas?
Each taxable entity formed in Texas or doing business in Texas must file and pay franchise tax.
What is the threshold for Texas franchise tax?
Tax Rates, Thresholds and Deduction LimitsItemAmountNo Tax Due Threshold$1,230,000Tax Rate (retail or wholesale)0.375%Tax Rate (other than retail or wholesale)0.75%Compensation Deduction Limit$400,0002 more rows
Do LLCs in Texas pay franchise tax?
Texas, however, imposes a state franchise tax on most LLCs. The tax is payable to the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts (CPA). In general terms, the franchise tax is based on an LLC's "net surplus" (the net assets of the LLC minus its members' contributions).
Do limited partnerships have to be registered in Texas?
While the partnership agreement is not filed for public record, the limited partnership must file a certificate of formation with the Texas Secretary of State. The Secretary of State provides a form that meets minimum state law requirements.
What is the Texas franchise tax threshold for 2022?
$1,230,000For the 2022 report year, a passive entity as defined in Texas Tax Code Section 171.0003; an entity that has total annualized revenue less than or equal to the no tax due threshold of $1,230,000; an entity that has zero Texas gross receipts; an entity that is a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) meeting the ...
Which of the following franchisees is subject to the franchise tax?
Franchise tax applies to corporations, partnerships, and many limited liability companies but does not apply to fraternal organizations, non-profits, and some limited liability corporations.
Which of the following franchisees is subject to the franchise tax?
Franchise tax applies to corporations, partnerships, and many limited liability companies but does not apply to fraternal organizations, non-profits, and some limited liability corporations.
Do trusts file Texas franchise tax?
The Texas franchise tax (also known as the “margin tax”) is so expansive that it can apply to private trusts administered in Texas. Every taxable entity is subject to the franchise tax, and the term “taxable entity” generally includes trusts, partnerships, limited liability companies, and corporations.
What is the Texas franchise tax threshold for 2022?
$1,230,000For the 2022 report year, a passive entity as defined in Texas Tax Code Section 171.0003; an entity that has total annualized revenue less than or equal to the no tax due threshold of $1,230,000; an entity that has zero Texas gross receipts; an entity that is a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) meeting the ...
Does Texas recognize disregarded entities?
Like many states, Texas allows for the formation of single member LLCs, and in fact, these entities are extremely common in this state. The IRS considers a single member LLC to be a disregarded entity. Essentially, this means that single member LLCs are taxed in the same way as sole proprietorships.
What is a series LLC?
A series LLC is treated as a single legal entity. It pays one filing fee and registers as one entity with the Texas Secretary of State. It files one franchise tax report and one Public Information Report as a single entity, not as a combined group, under its Texas taxpayer identification number. If one of the series has nexus in Texas, ...
What is a natural person?
Natural person means a human being or the estate of a human being. The term does not include a purely legal entity given recognition as the possessor of rights, privileges and responsibilities, such as a corporation, limited liability company, partnership or trust. Texas Tax Code (TTC) 171.0001 (11-a). Are family limited partnerships subject ...
Is a taxpayer a disregarded entity?
The taxpayer is a disregarded entity for federal purposes. If such a taxpayer has nexus in Texas, does the taxpayer have a Texas franchise tax filing responsibility? Yes. The legal formation of an entity – not an entity's treatment for federal income tax purposes – determines filing responsibility for Texas franchise tax.
Is a grantor trust taxable?
This subsection states that a grantor trust qualifies as a nontaxable entity if: all of the grantors and beneficiaries are natural persons or charitable entities and. it is not a trust taxable as a business entity pursuant to IRS Treasury Regulation Section 301.7701-4 (b).
Is a single member limited liability company a sole proprietor?
A single-member limited liability company filing as a sole proprietor for federal income tax purposes is a taxable entity. TTC 171.0002 (d). Is a non-Texas entity that owns a royalty interest in an oil or gas well in Texas subject to the franchise tax? Yes. A royalty interest in an oil or gas well is considered an interest in real property.
Is a family limited partnership taxable?
A family limited partnership is a taxable entity unless it meets the criteria of a passive entity under TTC 171.0003. Are sole proprietorships subject to the franchise tax? A sole proprietorship that is not legally organized in a manner that limits its liability is not a taxable entity. A single-member limited liability company filing as ...
Is a royalty interest in an oil well considered real property?
Yes. A royalty interest in an oil or gas well is considered an interest in real property. Therefore, a non-Texas entity that owns a royalty interest in an oil or gas well in Texas is considered to own real property in Texas and is subject to the franchise tax unless it is a nontaxable entity.
What are the advantages of a partnership?
An advantage to a partnership is the fact that partnerships do not pay taxes as a business; instead, the tax burden “passes through” to the individual members of the partnership. The partners pay the taxes.
What type of partnership is Texas?
The most common types are Limited Partnerships and Limited Liability Partnerships. That said, there are important nuances to these partnership types that make them troublesome for some entrepreneurs.
What is the biggest license requirement in Texas?
For most businesses, the biggest license requirement (beyond the state sales tax permit) is the industry-specific licenses and permits. For starters, Texas upholds all licenses required on the federal level. For example, business owners in industries like alcohol and agriculture need to get licenses from the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau and U.S. Department of Agriculture respectively.
What is partnership agreement?
A partnership agreement clearly defines the rights, privileges, and responsibilities of each member.
What happens if a partnership defaults on a loan?
If your partnership defaults on a loan or is sued for malpractice, you’ll (understandably) have to pay up. But if there’s not enough money in your business’s bank account to pay, your creditors can go after your personal assets. For example, they can lay claim to your car, your house, and your personal savings.
What is the sales tax rate in Texas?
That said, you will still have some tax burdens to take care of. For one thing, Texas still levies a sales tax. Currently the rate is 6.25%. Any business involved in retail sales will need to obtain a sales tax permit and then collect and pay that tax. Some counties can also add local charges onto the tax, too. You can read more about these local rates and start a permit application here.
Why do small businesses need an LLC?
For most small businesses, the LLC is ideal because it offers a lot of ownership flexibility, easy operation, and personal asset protection. If you’d like to learn more about forming an LLC in Texas, start with this guide.
What is a natural person?
A natural person is a human being as distinguished from a purely legal entity given recognition as the possessor of rights, privilege, and responsibilities , such as a corporation, limited liability company, partnership or trust. TTC 171.0001 (11-a).
Is a sole proprietorship taxable?
A sole proprietorship that is not legally organized in a manner that limits its liability is not a taxable entity. A single member limited liability company filing as a sole proprietor for federal income tax purposes is a taxable entity. TTC 171.0002 (d).
Is a passive entity taxable?
A passive entity as defined by TTC 171.0003 is not a taxable entity. TTC 171.0002 (b) (3). (See FAQ#8 under Passive Entities Rule 3.582 for possible reporting requirements.)
Do you have to file a separate franchise tax report in Texas?
Yes. The determination of responsibility for Texas franchise tax is based on the legal formation of an entity. An entity’s treatment for federal income tax purposes does not determine its responsibility for Texas franchise tax. Therefore, each taxable entity that is organized in Texas or doing business in Texas is subject to franchise tax, even if it is treated as a disregarded entity for federal income tax purposes. The entity is required to file a separate franchise tax report unless it is a member of a combined group. If the entity is a member of a combined group, the reporting entity may include the disregarded entity with the parent’s information; in that event, both entities are presumed to have nexus. (Updated 04/10/08)
Is a joint venture taxable?
No; a joint venture that is wholly and directly owned by natural persons is not a taxable entity. (Updated 06/19/08)
Is a limited liability company subject to franchise tax?
Yes; a limited liability company that is organized in Texas or is doing business in Texas is subject to the franchise tax. (Updated 06/19/08)
Is a partnership taxable?
Yes, to qualify as a non-taxable entity, the partnership must be a general partnership. TTC 171.0002 (b).
What is a general partnership?
A general partnership is created when two or more persons associate to carry on a business for profit. A partnership generally operates in accordance with a partnership agreement, but there is no requirement that the agreement be in writing and no state-filing requirement.
Where to file DBA in Texas?
If the business of the partnership is conducted under an assumed name (a name that does not include the surname of all of the partners), then an assumed name certificate (commonly referred to as a DBA) should be filed with the office of the county clerk in the county where a business premise is maintained in accordance with Section 36.10 of the Texas Business & Commerce Code.
What is a PLLC?
A professional limited liability company (PLLC) is an LLC that is formed for the purpose of providing professional services. Generally, professional services include personal services rendered by a dentist, attorney, physician, or veterinarian. PLLCs are treated similarly to LLCs for state and federal tax purposes.
What is sole proprietorship on tax return?
For federal tax purposes, a sole proprietor’s business activities are reported on Schedule C, Profit or Loss from Business . Accordingly, the sole proprietor’s business activities (income and losses) are reported directly on the sole proprietor’s individual income tax return.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of sole proprietorship?
Major advantages of operating as a sole proprietorship include ease of formation and management. A major disadvantage of operating as a sole proprietor is that the sole proprietor is liable for all of the debts and obligations of the business.
How are Texas corporations formed?
A Texas corporation is formed through the filing of a certificate of formation with the Texas Secretary of State. Corporations provide shareholders with limited liability—however, corporations are also subject to two levels of tax: first at the corporate level, [vii] and a second time at the shareholder level when dividends are distributed from the corporation to shareholders. [viii]
What is a limited partnership in Texas?
A Texas limited partnership is a partnership formed by two or more persons that has one or more general partners and one or more limited partners. Unlike a general partnership, a Texas limited partnership is only formed if a certificate of formation is filed with the Texas Secretary of State.
How are Texas limited liability companies formed?
A Texas limited liability company is formed through the filing of a certificate of formation with the Texas Secretary of State. Its management may either be through its members or through manager-members. See Tex. Bus. Org. Code § 101.251.
What is the most significant decision made by a business owner in Texas?
Perhaps the most significant of these decisions is the choice of entity the business will utilize while conducting its operations. Similar to many other states, the State of Texas offers its business owners and entrepreneurs several options. This Insight provides a summary of the tax and non-tax implications of each potential entity.
What is a taxable entity in Texas?
In addition, taxable entities include not only corporations and LLCs, but generally any entity with limited liability protection. Also introduced for the first time in Texas is the idea of unitary filing, something very alien to Texans. The only things that did not change are the due date of the tax, May 15 of each year, and the tax’s accounting period rules.
How is total revenue determined in Texas?
Total revenue is determined by extracting revenue from specific lines on the federal income tax forms (TX Tax Code §171.1011 (c) (1) (A)). Next, total revenue is reduced by applicable exclusions per Texas law. Exclusions tend to be based on industry, such as medical, legal, staff leasing services, and management companies (TX Tax Code §171.1011). Other exclusions include bad debt, income attributable to a disregarded entity, and net distributive income from partnerships and flowthrough partnerships (TX Tax Code §171.1011 (c) (1) (B)).
When to use tiered partnership?
Practice tip: The tiered partnership election should be used when the taxable entity is using the compensation deduction. Because some of the owners are other taxable entities, the lower-tier entity is not able to use the full compensation deduction through net distributive income. By making the election, the total tax paid by the lower- and upper-tier entities decreases. In addition, the upper-tier entities may elect to use either the deduction method or the E-Z method, even if the lower-tier entity does not use the same method, which could increase the tax savings even more. This is premised on the notion that the election need be available only at the lower level and not necessarily elected by the lower-level entity.
What is the most unsettled part of the passive entity test?
The most unsettled part of the passive entity test is the active income test. An active trade or business is conducted if the activities include one or more active operations that form part of the process of earning income or profit, and the entity performs active management and operational functions (TX Tax Code §171.0004 (a)). A potential problem arises for holding companies whose active trade or business is the receipt of passive income sources. With no clear explanation from the comptroller, tax exposure exists for these types of entities.
How to gain passive entity status?
Practice tip: For businesses selling real estate, one strategic plan is to form the entity as a partnership in order to gain passive entity status. Real estate entities should be passive entities as long as the sale of real estate results in a capital gain. Note that entities receiving real estate rental income should also be partnerships in case the real estate is sold for a capital gain. If a rental property is sold, it should be sold in the beginning of the year in order for the rental income to not be more than 90% of the total passive income for the tax year.
What is the exemption for franchise tax in Texas?
One of the most important exemptions for the Texas franchise tax is the exempt passive entity. Exempt passive entities will be required to file annual information statements to verify that the passive entity qualifications are met, but they will owe zero tax.
How much of a business can be derived from an active trade?
No more than 10% of the entity’s federal gross income can be derived from conducting an active trade or business.
What is a Passive Entity?
For purposes of the Texas franchise tax to be considered passive the entity must be a general partnership, limited partnership, limited liability partnership, or trust (excluding business trusts) for the entire period on which the franchise tax is based. It is also required that 90 percent of the entity’s federal gross income for the period must consist of the following sources of income:
What entity is required to file an informational report as a passive entity?
The previous rules required partnerships or trusts that were registered with the comptroller’s office or with the secretary of state’s office to file an informational report as a passive entity for the first reporting period that the entity qualified as passive.
What percentage of federal income is considered passive?
To be considered a passive entity, an entity may not receive more than 10 percent of its federal gross income for the period from the conduct of an active trade or business. In regards to conducting an active trade or business, the following activities do not constitute an active trade or business: Ownership of a royalty interest ...
Do you have to file a franchise tax return if you filed as passive in 2010?
The 2010 Instructions stated, as the Texas Administrative Code did at the time and until the Code was amended on June 28 of this year, that “an entity that filed as passive on a prior report will not be required to file a subsequent franchise tax report, as long as the entity continues to qualify as passive.”.
Do passive entities have to file taxes?
The section regarding the reporting and filing requirements was amended in several ways. First, the section was amended to state specifically that an entity that meets all the qualifications to be considered a passive entity owes no tax; however, the entity may be required to file a No Tax Due Report. Second, for passive entities (partnerships ...
Do you have to file a franchise tax report if a partnership is passive?
As long as the entity remained passive it would not have been required to file subsequent franchise tax reports. Under the old rules partnerships or trusts which qualified as passive entities and were never required (and had not) registered with the comptroller’s office or with the secretary of state’s office were not required to register with or file a franchise tax report with the comptroller’s office.
What is a dividend, interest, foreign currency gain, periodic and non-periodic payment?
Dividends, interest, foreign currency exchange gain, periodic and non-periodic payments with respect to notional principal contracts, option premiums, cash settlements or termination payments with respect to a financial instrument, and income from a limited liability company.

A (Very Important) Note on Personal Liability
- If you talk to a lawyer about your intentions to start a partnership, there’s a good chance he or she will tell you to be really careful. That’s because, from a legal standpoint, a partnership is not legally distinct from the individual partners behind the partnership. Granted, the business can obtain a bank account using the business’s name, enter...
5 Steps to Form Your General Partnership
- If you’re sure that a partnership is right for you, then your business starts as soon as you and your partner get to work. That said, there are 5 key steps you should complete to ensure your business gets off to a good start.
General Partnership Pros & Cons
- Before you form any business, you’ll want to do some careful soul-searching to ensure that entrepreneurship is right for you. That’s especially true for a general partnership. You’ll need to carefully evaluate the pros and cons before diving in.
Conclusion
- There are risks and challenges with a general partnership, but that doesn’t mean that you shouldn’t form one if it actually is the proper route for you. For the right business partners—and with the proper procedures—a general partnership offers exciting, unique opportunities.