
THE 4 TYPES OF FRANCHISE STRUCTURES
- · Area Developer [AD] - The right to open and operate multiple units within a designated geographic area. ...
- · Area Representative [AR] - The right to recruit third parties as unit franchisees, and/or provide support to third parties entering into unit agreements. ...
- · Sub-franchisor [Sub]—Grants unit franchises to third parties within a designated territory. ...
How to choose the right franchise structure?
- What speed of growth is required to meet your goals?
- What is your return at the unit level?
- How much support can you provide to your franchisees?
- Does your business lend itself to passive ownership?
- Are you able to cluster units effectively?
- How fragmented is the competitive market?
- What is the degree of competition for your targeted franchisee?
What are the basics of a franchise?
- The franchisee pays fees to the franchisor. ...
- The franchisor must have significant control over operations. ...
- While the franchisee may own a franchise, the services and products provided by the business are associated with the franchisor’s trademark.
What is the legal structure of a franchise?
The most common legal structure options are S-corporations, C-corporations, sole proprietorships, general partnerships and limited liability companies. S-corps are becoming more popular in recent years among franchisees due to the tax benefits afforded to smaller businesses with fewer stakeholders.
What are franchise relationship structures?
Understanding Franchise Relationship Structures. Franchising, at its core, is a way for a company to expand and distribute its products or services. In “Traditional Franchising,” product manufacturers use a downstream distribution system to get their products to market. In “Business Format Franchising,” companies sell the rights to use ...
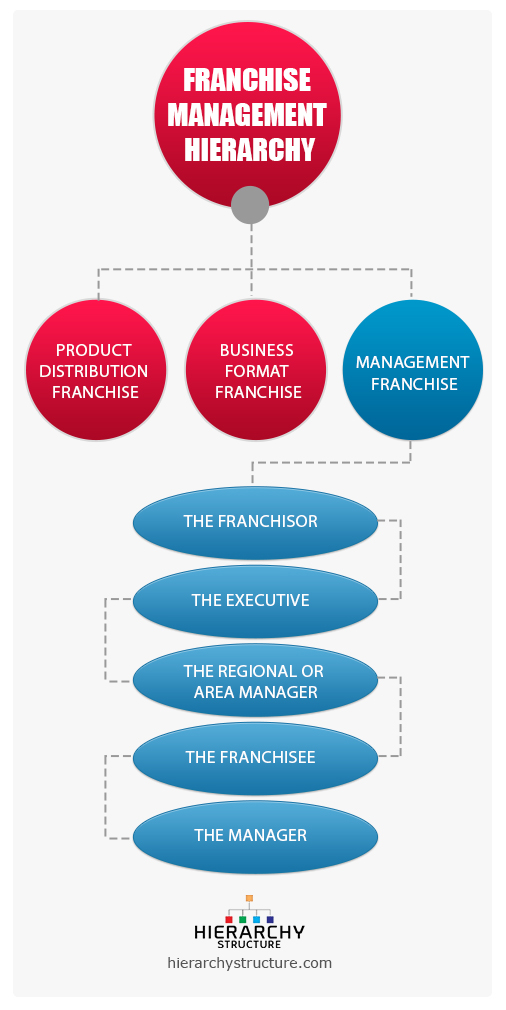
How are most franchises structured?
Determining the proper legal entity is a key factor that needs to be designated well before signing a franchise agreement. The most common legal structure options are S-corporations, C-corporations, sole proprietorships, general partnerships and limited liability companies.
What are the 4 types of franchise arrangement?
Below are four types of agreements franchised businesses commonly form.Single-Unit Franchise Agreement. In a single-unit agreement, the arrangement grants the franchisee the right to open and operate a single franchise unit. ... Multi-Unit Franchise Agreement. ... Area Development Franchise Agreement. ... Master Franchise Agreement.
What are 5 characteristics of a franchise?
8 Characteristics of Highly Profitable Franchises1) An excellent location. ... 2) A dedicated, involved franchisor. ... 3) A proven track record. ... 4) Little or no competition. ... 5) Recession-resistant. ... 6) Free of legal entanglements. ... 7) Not afraid of effective change. ... 8) Priced right.
What are the 3 conditions of a franchise agreement?
Franchise agreements vary between different franchises, but these seven areas should be addressed in every franchise agreement.Use of Trademarks.Location of the Franchise.Term of the Franchise.Franchisee's Fees and Other Payments.Obligations and Duties of the Franchisor.Restriction on Goods and Services Offered.More items...
What are the 3 basic types of franchising?
There are three main types of franchise opportunities available, these are: Business format franchises. Product franchises, or Single operator franchises. Manufacturing franchises.
What makes a successful franchise owner?
Franchise owners engage with people on a daily basis. Being personable and friendly are key factors for success. Positive interactions with customers, employees, vendors and the community are essential in developing those all-important relationships.
What makes a successful franchise?
Brand recognition and consistency are key elements to a successful franchise. Customers build trust and loyalty as they interact with the franchise, making it more likely they become repeat customers.
What makes a good franchise model?
Good franchisors have effective advertising materials, marketing approaches and know what media are the best option for their brand. If direct sales are an important part of their business model, training on effective networking and sales techniques should be provided.
What are the 4 types of franchising and give an explanation about it?
Learn the 4 main types of franchise arrangements: single unit, multi unit, area developer and master franchise. The franchising industry is very versatile, with multiple franchises, industry options and investment ranges. In addition, there is a diversity of types of franchise arrangements available.
What are the type of franchising agreements?
There are 4 basic types of franchise agreements: Single-unit, multi-unit, area development and master franchising. A single-unit franchise is the most common and is simply where a franchisor grants a franchisee rights to open and operate one single franchise unit.
What are the types of franchises?
The five major types of franchises are: job franchise, product franchise, business format franchise, investment franchise and conversion franchise.
What are the common franchise terms?
Here are a few common franchise terms that you should be aware of. A Franchisor is the owner of the franchise brand and business system. Franchisors can license their franchise to various franchisees. A Franchisee is a person or group who licenses the right to carry out business under a particular franchise trademark.
What is the element that we consider when we structure a franchise?
This is known as defining a territory . We will determine if you are giving a territory, how it’s figured out and what it looks like so it is fair for you and your franchisees. This leads us to determine if we are going to create incentives for franchisees to open more than one location.
What is a franchisee responsible for?
The franchisee is fully responsible for running and operating their own business. While there will be standards we set in place that your franchisees will be required to follow (such as what to use, purchase, sell and offer), your role is NOT to manage their daily operations. And when it comes to your specific methods, processes, formulas, ...
How to contact franchisees nationwide?
Call us directly at 1-877-615-5177 or send us your contact information and we will be happy to honestly answer all of your questions about how to structure a franchise.
Can a franchisee learn all trade secrets?
This means a franchisee could not just learn all your trade secrets and then decide to quit one day and start a competing business. While on the topic of setting standards for your franchise program, this includes what your franchisees are required to purchase and where to purchase from.
Is a franchisee an employee?
In franchising, your franchisees are independent business owners. They are NOT employees of you and you cannot treat them as such (see this article for more on the topic of your relationship with franchisees). The franchisee is fully responsible for running and operating their own business.
What Is a Franchise?
A franchise is a type of license that grants a franchisee access to a franchisor's proprietary business knowledge, processes, and trademarks , thus allowing the franchisee to sell a product or service under the franchisor's business name . In exchange for acquiring a franchise, the franchisee usually pays the franchisor an initial start-up fee and annual licensing fees .
What is franchise contract?
Franchise Basics and Regulations. Franchise contracts are complex and vary for each franchisor. Typically, a franchise agreement includes three categories of payment to the franchisor. First, the franchisee must purchase the controlled rights, or trademark, from the franchisor in the form of an upfront fee.
What Are the Risks of Franchises?
Disadvantages include heavy start-up costs as well as ongoing royalty costs. By definition, franchises have ongoing fees that must be paid to the franchisor in the form of a percentage of sales or revenue. This percentage can range between 4.6% and 12.5%, depending on the industry.
How Does the Franchisor Make Money?
Typically, a franchise agreement includes three categories of payment to the franchisor. First, the franchisee must purchase the controlled rights , or trademark , from the franchisor in the form of an upfront fee. Second, the franchisor often receives payment for providing training, equipment, or business advisory services. Finally , the franchisor receives ongoing royalties or a percentage of the operation's sales.
What does a franchisor receive?
Finally, the franchisor receives ongoing royalties or a percentage of the operation's sales. A franchise contract is temporary, akin to a lease or rental of a business.
How long does a franchise contract last?
It does not signify business ownership by the franchisee. Depending on the contract, franchise agreements typically last between five and 30 years, with serious penalties if a franchisee violates or prematurely terminates the contract.
When a business wants to increase its market share or geographical reach at a low cost, it may franchise its product?
When a business wants to increase its market share or geographical reach at a low cost, it may franchise its product and brand name. A franchise is a joint venture between franchisor and franchisee. The franchisor is the original business. It sells the right to use its name and idea. The franchisee buys this right to sell the franchisor's goods or services under an existing business model and trademark .
Why is the master franchisee structure used in international markets?
One reason this structure is frequently employed in international markets is that of the reduced franchisor interaction. You're instead relying on the master franchisee to provide regular training and support to the individual franchisees.
How does an area development franchise work?
In this franchise structure, the area developer signs a single franchise agreement for the rights to a predefined number of individual locations, which must be opened within a fixed amount of time. For instance, an area developer may sign a 10-unit contract for Dallas, Texas with the obligation that all 10 units must be open in no more than five years. The details of these agreements often vary from franchise to franchise, but all will have three predefined elements: number of units, territory and timeline.
Why are master franchising and area representative agreements not recommended for emerging franchisors?
Because master franchising and area representative agreements are highly complex and require a deep understanding of the inner workings of the franchise industry, especially from a legal perspective, these structures are not recommended for emerging franchisors. It's best for new franchisors to start at the individual level and introduce additional structures as the company grows and matures.
What is master franchise?
Master franchising , a structure most common in international markets, is an agreement in which the master franchisee is granted exclusive rights from the franchisor to sell individual franchises, often in a protected territory. Through this structure, the master franchisee collects a portion of the franchise fee in return for providing ongoing support to the individual franchisees, creating a responsibility buffer for the franchisor whose contractual obligations are only with the master franchisee.
What is single unit franchising?
While multiunit deals, area development agreements and conversions are attractive structures for franchisors, single-unit franchising is typically the recommended structure for most emerging franchisors. Individual franchise investors and owner-operators are often easier to target, and they can lend the best insight to help a franchisor understand what type of support future franchisees may need. Single-unit franchising also offers a franchisor the most control over franchise operations, and it helps you more easily identify which franchisees are performing well enough to potentially open additional locations.
What are the variables that you may encounter during the structuring phase?
Some variables you may encounter during the structuring phase include things like: Who is your target franchisee? What kind of support will they require? What sort of staffing demands will their operation produce? Further, the structure you choose will also influence your costs as you build your organization. So, be sure to allow yourself time for due diligence and thorough financial modeling.
What is Forbes Coaches Council?
Forbes Coaches Council is an invitation-only community for leading business and career coaches. Do I qualify?
What are the structures to consider when purchasing an existing franchise?
These include: operating as a sole trader, a partnership, a company, a two-tiered company structure or through a trust. This article considers the advantages and disadvantages of each franchise business structure.
What is franchising in business?
In the case of a franchise system, it is common for the franchisor to be the owner of the intellectual property of the business. They will then license this to your company for use in operating the franchise. This means that these more valuable assets would not be at risk if your company fails.
What is franchise trust?
Franchise Trust Structure. The final structure to consider operating your franchise through is a trust. There are two different types of trusts, discretionary (family) or unit trusts. With either trust type, there is a trustee that owns the assets of the business and operates the business on behalf of the trust.
Why do companies have two tiered companies?
Some businesses decide to set up a two-tiered company structure to protect the valuable assets of the business. This is usually done through a holding company and operating company relationship. The holding company owns the assets and intellectual property of the business and the subsidiary company is the operating company.
Why do trusts have to distribute profits?
The trust must distribute the profit/income of the trust to the beneficiaries each financial year to avoid paying the highest tax rate. This can be a problem if your business needs working capital or wants to attract investment.
What happens if you wind up a company?
If you needed to wind up the company, you could potentially lose all of the business’ assets. This is important to consider if you want to have these assets for future use.
Is a franchise a separate entity?
Setting up a proprietary limited company to operate a franchise will protect your personal assets, as a company is a separate legal entity. It is capable of owning its own assets and liabilities and entering into contracts on behalf of the franchise. It is a more straightforward structure to operate than a two-tiered company or trust.
What is a Franchise Business?
Let’s break down what a franchise business is and discuss other common words associated with franchising.
What does a franchise agreement include?
So, how does a franchise agreement work? In addition to laying out what type of franchise license will be issued to the franchisee, a franchise agreement must also include a franchise disclosure document. This document must include 23 key items, as dictated by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). The FTC also requires that franchisors must provide franchisees with these provisions at least 14 days before the document needs to be signed—or before any initial money is exchanged. The 23 sections of the franchise disclosure document are:
What are the key factors in the franchise relationship?
Both the franchisor and franchisee should maintain regular, honest communication about goals, successes, and pitfalls.

What Is A Franchise?
- A franchise is a type of license that grants a franchisee access to a franchisor's proprietary business knowledge, processes, and trademarks, thus allowing the franchisee to sell a product or service under the franchisor's business name. In exchange for acquiring a franchise, the franchisee usually pays the franchisor an initial start-up fee and annual licensing fees.
Understanding Franchises
- When a business wants to increase its market share or geographical reach at a low cost, it may franchise its product and brand name. A franchise is a joint venture between a franchisor and a franchisee. The franchisor is the original business. It sells the right to use its name and idea. The franchisee buys this right to sell the franchisor's goods or services under an existing business m…
Franchise Basics and Regulations
- Franchise contracts are complex and vary for each franchisor. Typically, a franchise agreement includes three categories of payment to the franchisor. First, the franchisee must purchase the controlled rights, or trademark, from the franchisor in the form of an upfront fee. Second, the franchisor often receives payment for providing training, equip...
Pros and Cons of Franchises
- There are many advantages to investing in a franchise, and also drawbacks. Widely recognized benefits include a ready-made business formula to follow. A franchise comes with market-tested products and services, and in many cases established brand recognition. If you're a McDonald's franchisee, decisions about what products to sell, how to layout your store, or even how to desig…
Franchise vs. Startup
- If you don't want to run a business based on someone else's idea, you can start your own. But starting your own company is risky, though it offers rewards both monetary and personal. When you start your own business, you're on your own. Much is unknown. "Will my product sell?", "Will customers like what I have to offer?", "Will I make enough money to survive?" The failure rate for …